Hyperspectral
Hyperspectral imaging is a technique that combines both conventional imaging and spectroscopy. This technology enable the acquisition of both the spatial and spectral information of an object. Hyperspectral remote sensing consists in the simultaneous acquisition of images in many narrow and contiguous spectral bands. Each pixel in the remotely acquired scene has an associated spectrum depending on the material of the target surveyed.
Hyperspectral imagery is typically collected and represented as a data cube (Hyperspectral Cube). The data is visualized as a volume, with spatial information collected in the X-Y plane, and a third dimension (Z-direction) representing the contiguous spectral bands of the image.
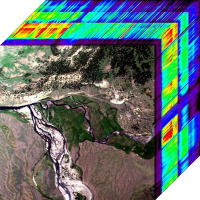
There are many environmental components that can be studied using hyperspectral remote sensing data:
- Atmosphere: water vapor, cloud properties, aerosols
- Water: quality, pollution
- Land use: soil types, pattern recognition, land use changes
Other fields of research involved are:
- Ecology: chlorophyll, leaf water, cellulose, pigmemts, lignin
- Geology: mineral types
- Snow/Ice: snow cover fraction, grainsize, melting
- Biomass burning: subpixel temperatures, smoke
- Materials: mineral exploration, agriculture and forest production


